Inheritance Internal mechanism in java
Internal Mechanism to support inheritance in java
In the evolution of language First came C => C++ => JAVA.
Java Virtaul machine specification provides lot of details of the internal mechanism, here we present a very naive way of how inheritance is supported internally.
Key Take Aways :
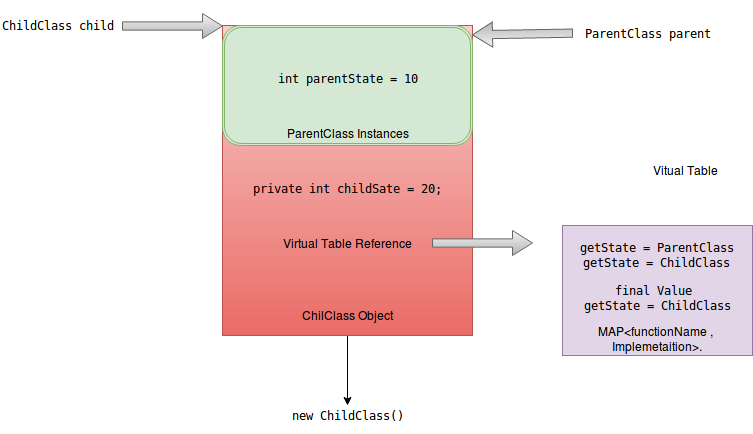
- Every Java object has a virtual Table pointer along with its own instance members.
- The base class Instance members are placed at start and then follows the member of Sub class.
- The virtual table pointer of the object has the entries for all the functions associated with the class.
- Irrespective of you point to a object using base class or sub class reference , the virtual table reference is known by both type of references.
- The reason why using a reference of base class on a sub Class objects works is , the Sub Class has a bigger memory footprint as compared to base class.
- The base class reference is only aware of the instance members and methods defined in its class.
class ParentClass { protected int parentState = 10; public String getState(){ return "parentState value is " + parentState; } } public class ChildClass extends ParentClass{ private int childSate = 20; @Override public String getState(){ return "childSate value is " + childSate; } public static void main(String[] args) { // parent refrence pointing to the child class ParentClass parent = new ChildClass(); System.out.println("Parent class method call output is : " + parent.getState()); System.out.println("state field value of parent is : " + parent.parentState); ChildClass child = (ChildClass) parent; System.out.println("Child class method call output is :" + child.getState()); } } OutPut is : Parent class method call output is : childSate value is 20 state field value of parent is : 10 Child class method call output is :childSate value is 20
[addToAppearHere]
Key take Aways :
- For methods the concept of virtual pointers and table exist hence overriding works on methods.
- For instance fields no such mechanism exist hence fields can be hide but never overriden.
- Static methods or fields are not part of object hence they never participate in Inheritance and can only be hide.
- Using Reference of parent on child object only enables the parent to access the region marked “logically” as parent.
- The logical marking is done by calculating the size of instance members in the parent class when .class file is being generate.
- if one uses javap -v on the generated class one can see invokevirtual call in the generated code.